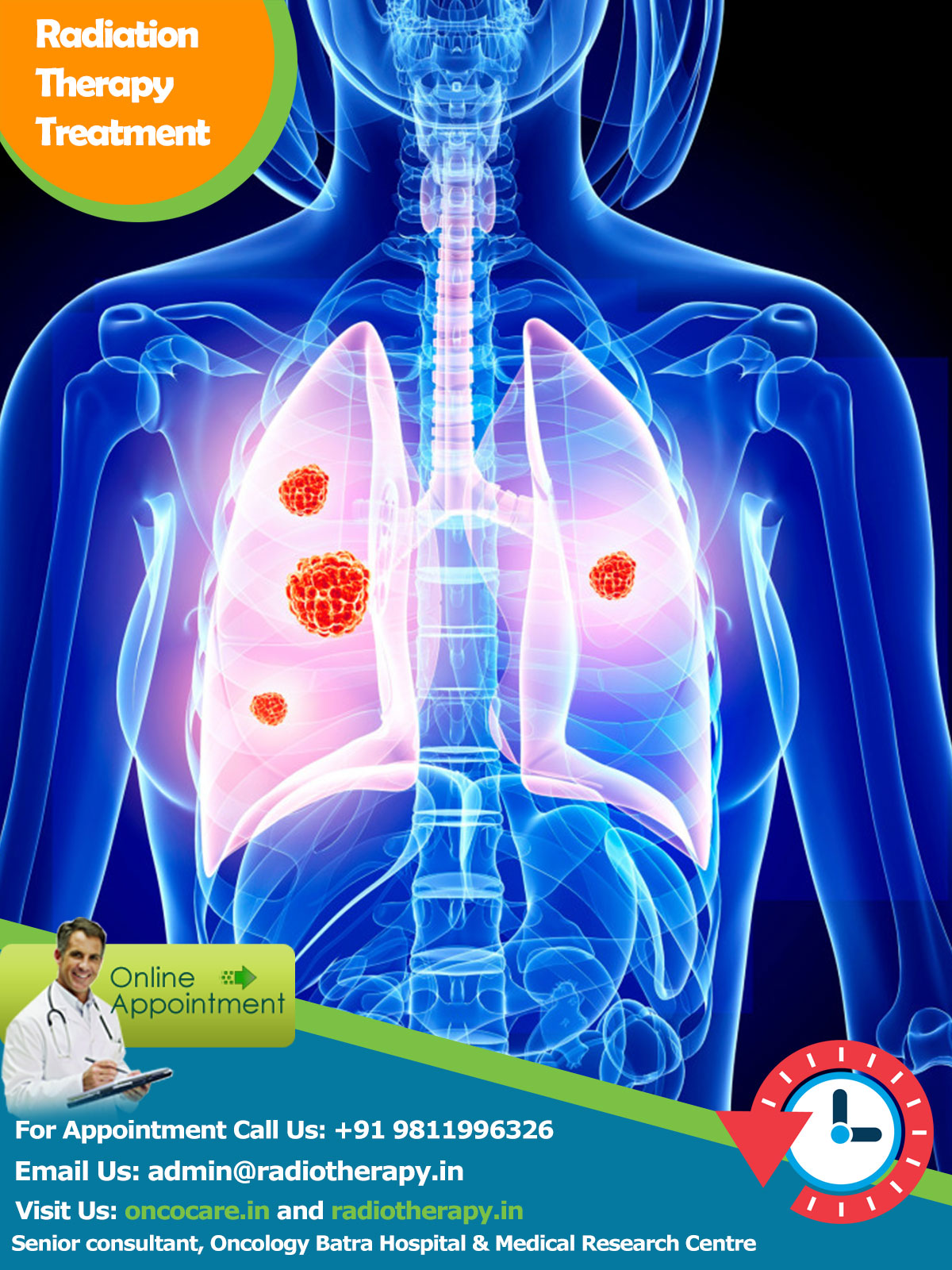
NSCLC Treatment in India, Lung cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells that start off in one or both lungs; usually in the cells that line the air passages. The abnormal cells do not develop into healthy lung tissue, they divide rapidly and form tumors. As tumors become larger and more numerous, they undermine the lung’s ability to provide the bloodstream with oxygen. Tumors that remain in one place and do not appear to spread are known as “benign tumors”. Malignant tumors, the more dangerous ones, spread to other parts of the body either through the bloodstream or the lymphatic system. Metastasis refers to cancer spreading beyond its site of origin to other parts of the body. When cancer spreads it is much harder to treat successfully. Primary lung cancer originates in the lungs, while secondary lung cancer starts somewhere else in the body, metastasizes, and reaches the lungs. They are considered different types of cancers and are not treated in the same way. According to the National Cancer Institute, by the end of 2015 there will have been 221,200 new lung cancer diagnoses and 158,040 lung-cancer related deaths in the USA. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 7.6 million deaths globally each year are caused by cancer; cancer represents 13% of all global deaths. As seen below, lung cancer is by far the number one cancer killer.
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an oncologist.[1] The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄνκος (ónkos), meaning "tumor", "volume" or "mass"
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a category of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs), or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms (palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of medical oncology
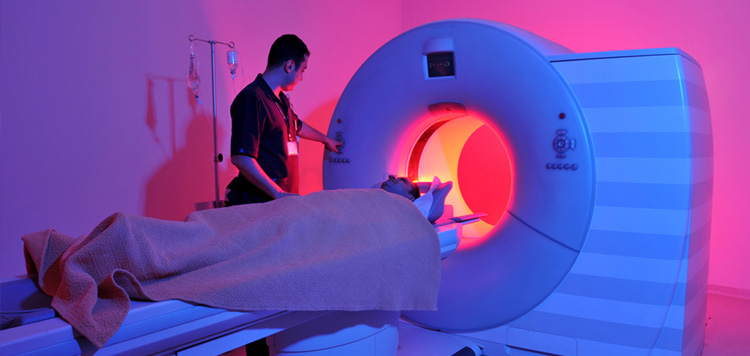
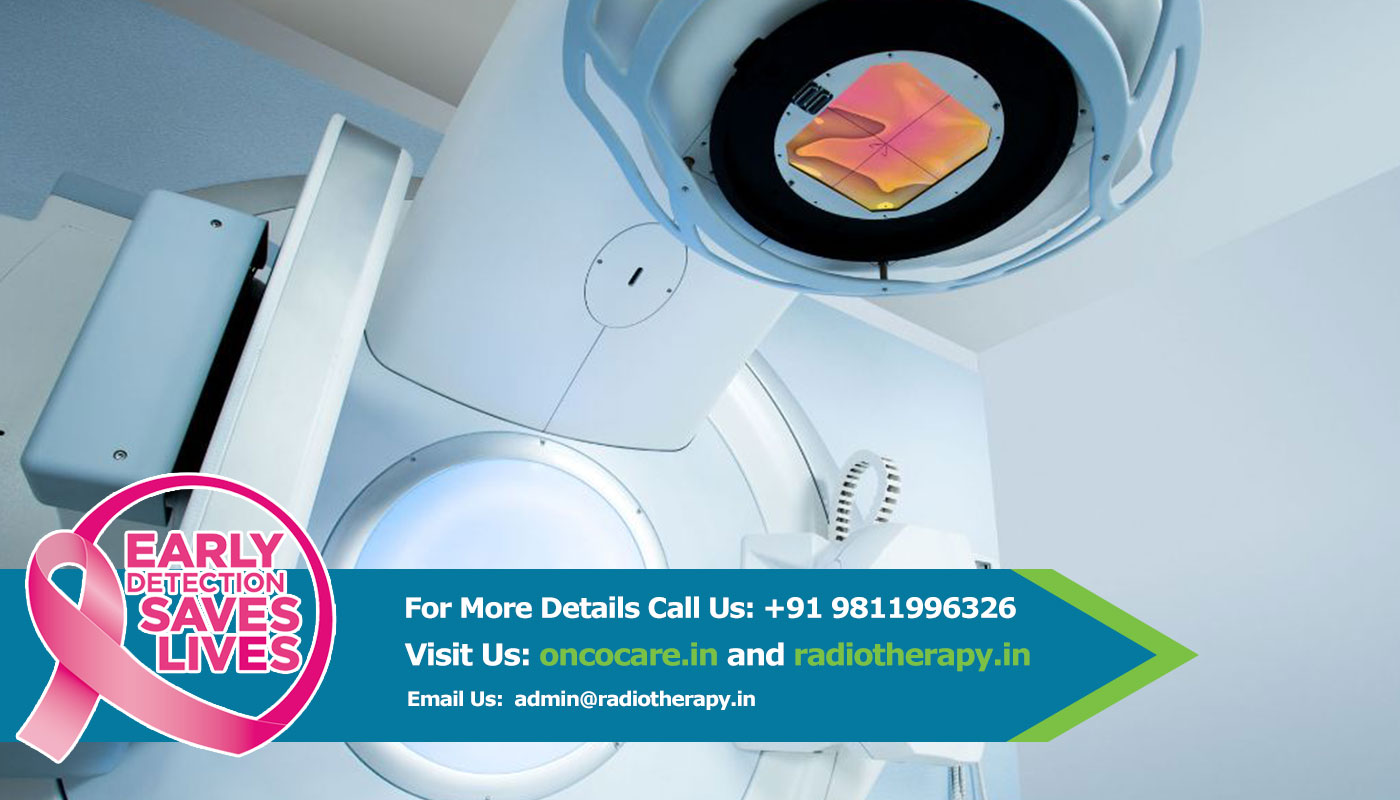
Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to shrink tumors and kill cancer cells (1). X-rays, gamma rays, and charged particles are types of radiation used for cancer treatment.
The radiation may be delivered by a machine outside the body (external-beam radiation therapy), or it may come from radioactive material placed in the body near cancer cells (internal radiation therapy, also called brachytherapy).Systemic radiation therapy uses radioactive substances, such as radioactive iodine, that travel in the blood to kill cancer cells.
About half of all cancer patients receive some type of radiation therapy sometime during the course of their treatment.
Skin cancer is a common, usually low-grade cancerous (malignant) growth of the skin. It starts from cells that begin as normal skin cells and transform into those with the potential to reproduce in an out-of-control manner. Unlike other cancers, the vast majority of skin cancers have no potential to spread to other parts of the body (metastasize) and become life-threatening. The “ground breaking” ‘liquid biopsy’ blood test promises to speed up the diagnosis of melanoma, ensuring patients get the personalised treatment they need sooner, researchers said.
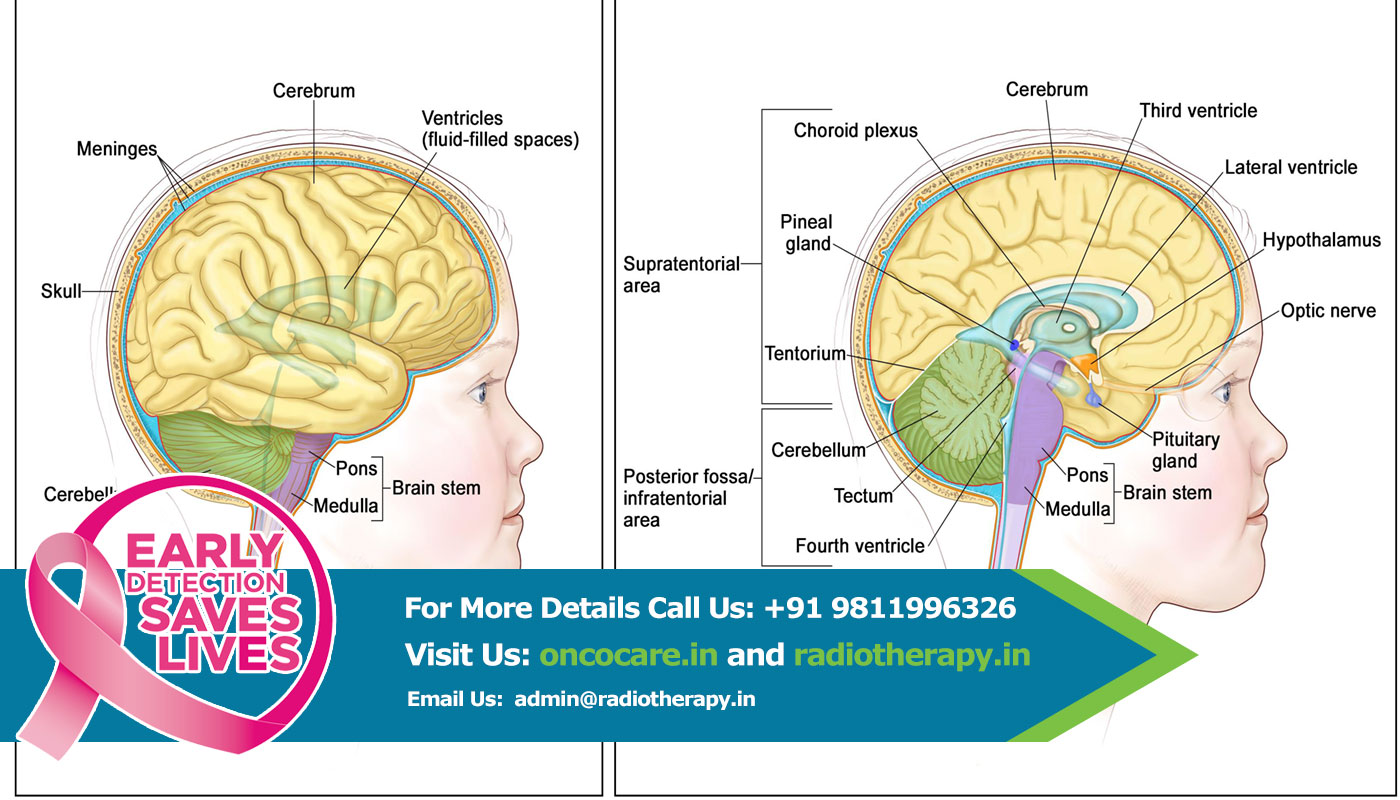
Astrocytomas are a type of cancer of the brain. They originate in a particular kind of glial cells, star-shaped brain cells in the cerebrum called astrocytes. This type of tumor does not usually spread outside the brain and spinal cord and it does not usually affect other organs. Astrocytomas are the most common glioma and can occur in most parts of the brain and occasionally in the spinal cord.
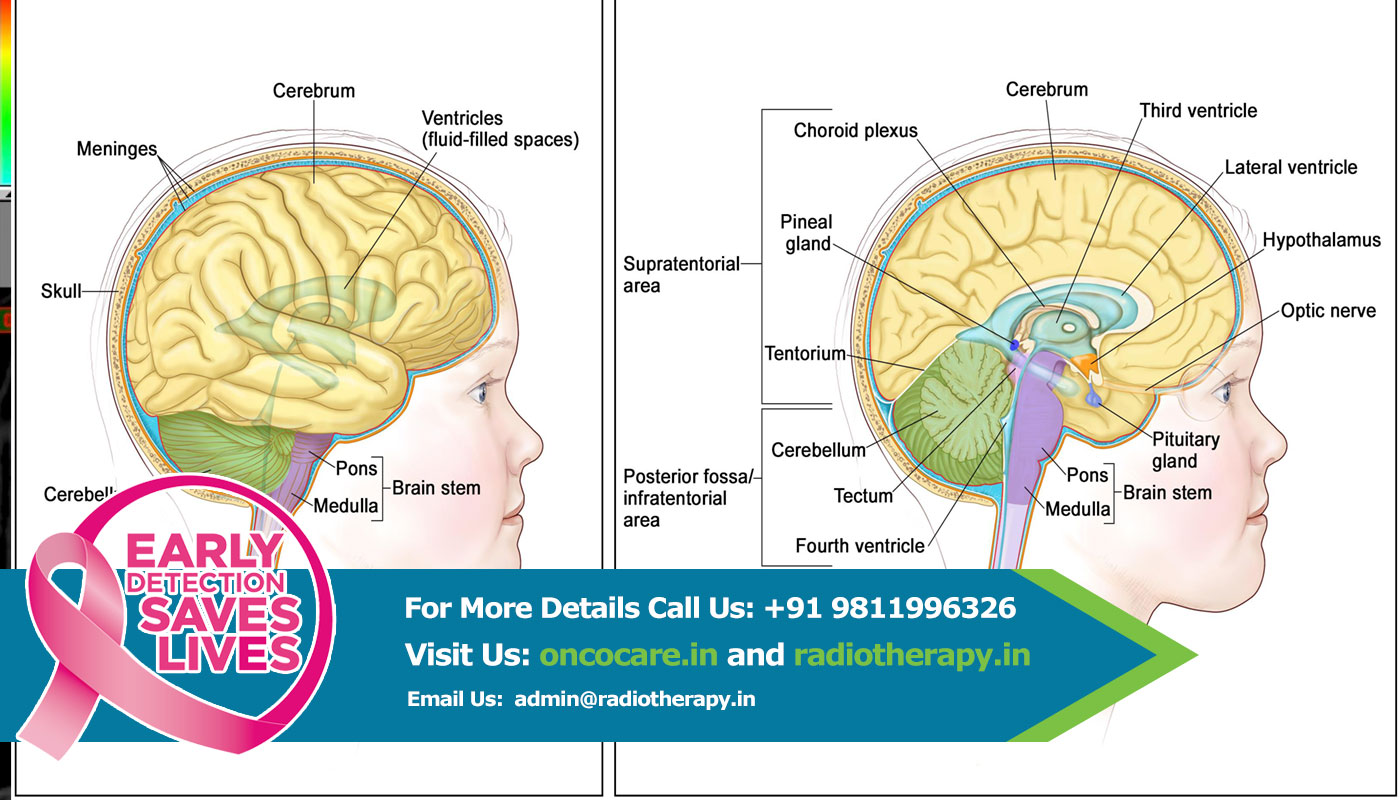
“Glioma” is a general term used to describe any tumor that arises from the supportive (“gluey”) tissue of the brain. This tissue, called “glia,” helps to keep the neurons in place and functioning well.
There are three types of normal glial cells that can produce tumors. An astrocyte will produce astrocytomas (including glioblastomas), an oligodendrocyte will produce oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas come from ependymal cells.